Sustainable Web Design: Building a Greener Future
Table of Contents
TLDR
This article delves into sustainable web design and its significant role in creating a more environmentally friendly online future.
It discusses the importance of acknowledging the impact of digital activities, particularly website design, on the environment as global awareness of environmental issues increases.
It delves into strategies for creating sustainable digital products and services, aiming to diminish their environmental impact and contribute to a greener future.
Embracing Sustainability
Sustainability has become a pressing concern across many industries. As our awareness of environmental issues grows, it’s essential to recognise the significant impact that the digital sphere, particularly web design, has on our planet. This article explores sustainable web design and its pivotal role in creating a greener online future.

QUICK FACTS
- The internet contributes about 3.7% of global greenhouse emissions, which is comparable to the airline industry.
- Emissions are predicted to double by 2025 This includes the energy use of electronic devices, data centres and the transportation of internet traffic.
The Importance of Sustainable Web Design
With the rapid expansion of the internet and the ever-increasing number of websites, the digital world’s energy consumption and carbon footprint have skyrocketed. Traditional web design practices often neglect ecological considerations, resulting in excessive energy use, resource wastage, and environmental degradation.
But there is a better way. Sustainable web design presents a transformative solution that aligns digital experiences with environmental responsibility. By integrating eco-conscious practices and thoughtful design, we can mitigate the environmental impact of websites while delivering exceptional user experiences.
Today, people want more from brands beyond selling products; they seek alignment with their own values and morals, and climate change is now a hot topic that’s of concern to us all. We are seeing an increasing number of clients wanting to achieve carbon neutrality as part of their sustainable web manifesto. When creating websites, considering low energy consumption during the design and development process is more important than ever.
QUICK FACTS
- Research suggests the internet’s electricity usage by 2025 would make it the 4th largest country in terms of consumption.
- The IT sector’s energy footprint is already estimated to account for about 7% of global electricity consumption, as reported by Greenpeace.
• • •
Understanding Sustainable Web Design
Defining Sustainable Web Design
Before diving into sustainable web design strategies and practices, it’s important to have a solid understanding of its definition and core principles.

What is Sustainable Web Design?
Sustainable web design is centred around crafting websites that reduce their harmful effects on the environment and maximise their positive contributions to sustainability. It involves integrating environmentally friendly practices throughout the entire design and development process, covering everything from initial planning and coding to hosting and ongoing maintenance.
The Core Principles of Sustainable Web Design
To effectively implement sustainability, it’s essential to adhere to the following core principles:
1. Energy Efficiency
Prioritising techniques and technologies that lower energy use, such as optimising code, using efficient servers, and implementing caching strategies.
2. Resource Optimisation
Minimising resource usage by reducing file sizes, compressing images, and adopting efficient coding practices to reduce bandwidth and server load.
3. User-Centric Approach
Designing websites with a focus on delivering an exceptional user experience, ensuring fast loading times, intuitive navigation, and easily accessible content.
4. Accessibility and Inclusivity
Ensuring that web pages are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities, by following accessibility standards and guidelines.
5. Ethical Hosting
Selecting hosting services that use renewable energy, like solar or wind power, for their data centres (the places where website information is stored). This choice helps in reducing the environmental impact of websites.

The Environmental Impact of Traditional Web Design Practices
Traditional web design practices often prioritise aesthetics and functionality over environmental considerations. Unfortunately, this approach can result in significant negative environmental impacts, including:
- High energy use due to inefficient coding and resource-intensive technologies.
- Excessive use of server resources, leading to increased carbon emissions.
- Large file sizes and unnecessary data transfers, resulting in higher bandwidth usage and energy use.
- Lack of consideration for accessibility, excluding individuals with disabilities from accessing content.
Understanding the environmental consequences of traditional web design highlights the urgency and significance of adopting sustainable practices.
In the next section, we will explore key strategies and techniques that enable designers to create sustainable websites while minimising their environmental footprint.
• • •
Key Strategies for Sustainable Web Design
Optimising Energy Efficiency
Energy efficiency plays a vital role in sustainable web design, as reducing energy use contributes to a greener online future. Web designers can optimise energy efficiency in their projects by implementing the following strategies:
1. Efficient Coding and Scripting
By writing clean and streamlined code, developers help minimise the processing power required to display pages. Techniques like code minification, removing unnecessary scripts, and caching methods can significantly reduce energy use.
2. Responsive Design for Mobile Devices
Designing responsive websites that adapt to different screen sizes and device capabilities enhances energy efficiency. Mobile-optimised designs use fewer resources while delivering an optimal user experience.
3. Sustainable Hosting and Server Selection
Storing files on physical servers in data centres continuously consumes energy. Choosing hosting providers that prioritise renewable energy sources and employ energy-efficient servers is vital. Opting for eco-friendly hosting solutions can significantly reduce the carbon footprint associated with hosting. Choosing a hosting company with data centres closer to the site’s core audience minimises data transfer distances and reduces energy use.
Minimising Resource Usage
Reducing resource usage not only contributes to sustainability but also improves performance. Here are key strategies to achieve greater resource efficiency:
1. File Compression and Optimisation
Compressing images, CSS files, and JavaScript resources reduces file sizes and bandwidth usage. Techniques like lazy loading images and code minification further improve resource efficiency. Opting for next-gen image formats such as WEBP often provides better compression than PNG or JPEG, which means faster downloads and less data consumption. Scalable vector graphics (SVGs) are built using data points and code, resulting in significantly smaller file sizes that can scale to different screen sizes without losing quality.
—
According to HTTP Archive, images, on average, make up 21% of the total weight of a web page.
—
2. Efficient Content Delivery
Implementing content delivery networks (CDNs) and caching techniques improves performance by delivering content from servers closer to users. This reduces the distance data travels, resulting in faster load times and lower energy use.
3. Dark Mode
The colours used on a website can impact the power consumption of a user’s device. Some colours, particularly white and blue, demand more light to display, making them particularly power-hungry. Darker colours can significantly reduce battery usage, so consider offering a dark mode option for your website.
—
Darker colours can reduce battery usage by up to 63% on AMOLED displays, even at maximum brightness. – Night Eye
—
4. Typefaces
The type of font used can influence how much energy the site uses. Some fonts are ‘heavier’ than others (a single weight can add up to 250kb to a website), meaning they take up more space and energy. To optimise for energy consumption, keep these points in mind:
- Using system fonts pre-installed on devices, unlike custom fonts, will avoid loading additional files.
- Online-hosted fonts, like Google fonts, allow websites to access the same file instead of uploading multiple versions.
- Minimising font variations will reduce the impact on your site.
- Variable fonts like Inter contain multiple style variations within a single font file.
- Opt for file formats like WOFF for smaller file sizes and better performance than OTF or TTF files.
5. Search Engine Optimisation
Every time a user performs an internet search, it generates approximately 7g of CO2 emissions – Alex Wissner-Gross, Envionmental Fellow at Harvard University
Optimising a website not only enhances its Google ranking but also aligns with users’ search intent, ultimately leading to a more sustainable web environment.
By focusing on page speed and overall web performance, websites can ensure pages load faster, offering a better user experience. One effective strategy to achieve this is by reducing the file size of image files, which can result in huge savings in terms of bandwidth and power consumption.
This approach not only makes a website more appealing to search engines for efficient indexing but also minimises the energy required for crawling and indexing processes.
Given the vast number of searches conducted daily, the impact of such optimisations is significant, contributing to the sustainability of digital products and services.
6. Mobile-first Design
Embracing a mobile-first design approach holds significant potential for enhancing online sustainability. By starting the design process from small screens and gradually scaling up, the focus shifts to elements that work efficiently within limited space.
Following Luke Wroblewski’s advice, mobile-first design compels us to prioritise essential content and actions before expanding to larger screens.
Sustainable Web Design highlights that a mobile-first approach discourages users from loading large assets intended for desktop use, further promoting sustainable practices.
In 2022, the global average of all website visits from mobile devices was 56.86%
Source: Statista.com

Emphasising User Experience
User Experience (UX) and sustainability go hand-in-hand. By prioritising user-centricity, designers can enhance user satisfaction and sustainability. Consider the following approaches:
1. Streamlined Navigation and Intuitive Design
Well-structured sites with intuitive navigation help users find information quickly, reducing the time and energy needed to achieve their goals. Clear calls-to-action and logical page layouts contribute to an efficient user experience.
2. Performance Optimisation
Fast-loading pages not only improve user experience but also reduce energy use. Techniques like image optimisation, browser caching, and code minification enhance website performance and sustainability.
3. Accessibility for All Users
Incorporating accessibility features ensures that web pages are usable by individuals of all abilities. By following accessibility standards and guidelines, designers can create inclusive experiences that cater to a broader audience, promoting sustainability through inclusivity.
Using high-contrast colours makes the information displayed more defined, so viewers won’t need to increase the brightness on their device, saving battery power.
—
Reducing screen brightness by 20% on some phones can cut energy consumption in half.
—
Incorporating these key strategies into projects empowers designers to create sustainable websites and digital products that deliver exceptional user experiences while minimising their environmental impact.
• • •
Case Studies and Examples
Sustainable Web Design Examples
Real-life examples of sites implementing sustainable design practices can provide valuable insights and inspiration for designers. The following case studies and examples highlight the positive impacts:
1. The World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
WWF UK uses renewable energy hosting, resource-efficient technologies, and an optimised, responsive design. Its focus on education about environmental issues further enhances its role as a model for sustainable web design.
- Renewable Energy Hosting: The WWF site is hosted on servers powered by renewable energy. This significantly reduces the environmental impact of the website’s operations, aligning with sustainable practices.
- Resource-Efficient Technologies: The site uses technologies like Vue.js, which are less resource-intensive than some alternatives. This reduces CPU and memory usage, enhancing the site’s energy efficiency.
- Optimised Page Design: Pages are designed to be as small as possible without compromising usability. This approach helps in reducing data transfer when pages load, saving energy.
- Mobile Responsiveness: The design is responsive, efficiently catering to various devices and screen sizes. This responsiveness is crucial for reducing energy and resource use, especially for mobile users.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity: It appears to follow accessibility standards, ensuring that it is usable by individuals of all abilities. This practice fosters inclusivity and contributes to sustainability by making the site more efficient and reducing the need for increased brightness or additional resource usage.
- Educational Content: The site educates visitors about sustainability and environmental conservation. This content raises awareness and promotes sustainable practices among its audience.
- User Experience (UX): The site provides a streamlined user experience with intuitive navigation and clear calls-to-action (CTAs). This efficiency reduces power consumption, as users can find information quickly without unnecessary page loads.
2. Clearstone Energy
Clearstone Energy, a company specialising in renewable energy solutions, is strongly committed to sustainability, which extends to its digital presence. In an industry focused on clean energy, Clearstone Energy must embody these principles in every aspect of its operations, including its website.
Clearstone’s homepage is cleaner than 66% of pages tested at websitecarbon.com. Only 0.31 g of CO2 is produced whenever someone visits this page.
By adopting the following practices, Clearstone Energy demonstrates that companies in the renewable energy sector can lead by example:
- Clean and Efficient Design:
- Clearstone Energy features a clean, straightforward design that emphasises efficiency. The streamlined approach to design reduces the amount of data that needs to be loaded each time a page is accessed, thereby saving energy.
- Optimised Imagery:
- The website uses well-optimised images. These images are carefully compressed to reduce file sizes without compromising quality, resulting in less bandwidth usage and reduced powe consumption both on the server side and for end users.
- Accessibility and Inclusivity:
- The website design incorporates accessibility features, ensuring it is navigable and usable by individuals with various abilities. This practice aligns with sustainable principles by making the site efficient and reducing the need for increased screen brightness or additional resource usage.
- Mobile Optimisation:
- Recognising the growing trend of mobile internet usage, Clearstone Energy’s website is optimised for mobile devices. This ensures efficient loading and functioning on smaller screens, reducing unnecessary data usage and energy use.
- Use of Sustainable Hosting Services:
- Aligning with its core business, Clearstone Energy utilises green hosting services that prioritise renewable energy sources. This choice significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with hosting.
3. Orbus Software
Orbus Software is a global software vendor and a leading provider of solutions for digital transformation and enterprise architecture. A range of features and best practices collectively contribute to minimising the environmental impact of its website, aligning with their broader goals of corporate social responsibility and environmental stewardship.
- Efficient and Clean Design: The website features a clean and straightforward design, reducing the amount of data that needs to be loaded, thus saving energy.
- Image Optimisation: The images on the site are well-optimised and consume less bandwidth, contributing to lower energy use both on the server side and for the end user.
- Light and Dark Modes: Orbus include a switch to enable dark mode in the header of every page. This enhances user experience by making browsing in low-light conditions far more comfortable, allowing viewers to find information more readily while consuming less energy.
- Accessibility: The website has been designed with accessibility in mind, using clear, readable fonts and a navigable layout, which is an essential aspect of sustainable design, ensuring the site is usable for all, including those with disabilities.
- Mobile Responsiveness: The website has been optimised for mobile users, ensuring efficient loading and functioning on small-screen devices and reducing unnecessary data usage and energy use.
- Modern Web Technologies: The website utilises modern technologies for better performance and efficiency, including efficient coding practices, CDN (Content Delivery Network) for faster delivery and optimised JavaScript and CSS. This backend optimisation helps Orbus achieve faster load times and less power consumption during access.
4. The Guardian
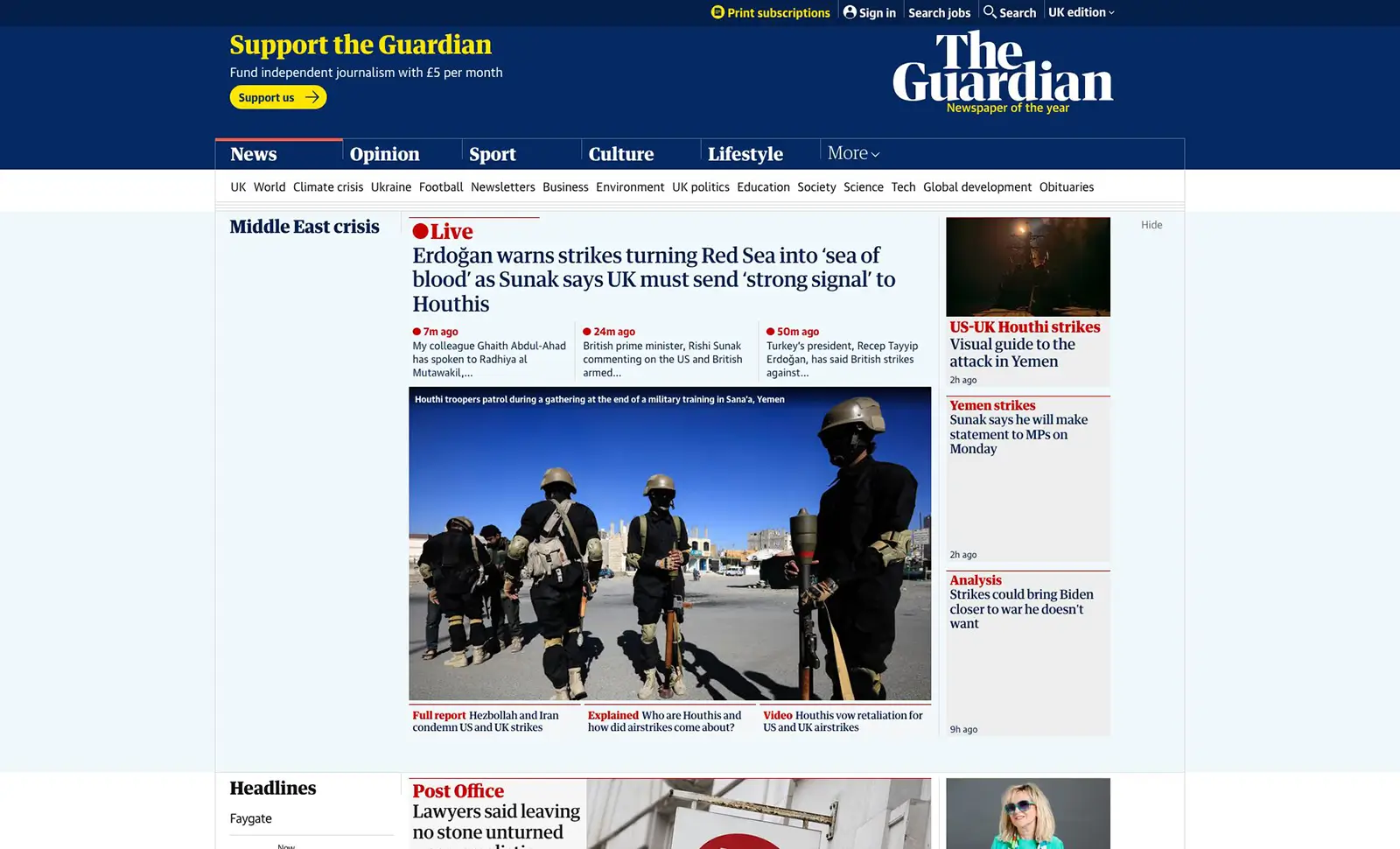
The Guardian is committed to reducing its digital carbon footprint while managing the high traffic demands typical of a major news website. Recognising the environmental impact of online activities, The Guardian has taken proactive steps to integrate sustainability into its design and operations. Their approach demonstrates that high-traffic websites can balance operational demands with environmental responsibility, paving the way for a more sustainable digital future.
Sustainable Web Design Practices:
- Optimised Content Delivery:
- The Guardian employs advanced content delivery network (CDN) strategies to reduce the distance data travels, ensuring faster loading times and lower energy use. This method not only enhances the user experience but also significantly cuts down on the energy used to transmit information across the globe.
- Energy-Efficient Servers:
- Understanding the importance of energy use in data centres, The Guardian uses servers optimised for energy efficiency. These servers are designed to handle large amounts of data and user requests with minimal energy use, reducing the overall carbon footprint of the website.
- Image and Video Optimisation:
- As a news outlet, The Guardian frequently uses multimedia content. To reduce the site’s impact, images and videos are carefully optimised to maintain quality while reducing file sizes. This practice lowers the amount of data transferred and energy consumed during loading.
- User Engagement with Sustainability:
- The Guardian doesn’t just practice sustainability; it actively engages its readers on the subject. The website includes sections dedicated to environmental reporting and discussions about climate change, raising awareness about sustainability issues.
- Responsive and Efficient Design:
- The site’s responsive design adapts seamlessly to different devices, from desktops to smartphones. This approach ensures the site uses only the necessary resources for each device, avoiding wasteful energy use, especially on mobile devices.
- Regular Performance Audits:
- The Guardian conducts regular audits of its website performance and energy efficiency. This ongoing evaluation allows them to continually refine their strategies and implement the latest sustainable technologies.
Lessons Learned and Impact Achieved
These case studies highlight the successful integration of sustainable design principles in various industries. They showcase how sustainability can be seamlessly woven into the digital experience, benefiting both the environment and the user.
By adopting sustainable practices, these organisations have achieved the following positive impacts:
- Reduced energy use and carbon emissions associated with website operations.
- Improved website performance, resulting in faster loading times and better user experiences.
- Increased awareness and engagement among users by showcasing their commitment to sustainability.
- Contributed to a broader movement towards a greener, more sustainable online future.
These examples demonstrate the immense potential of sustainable design to create meaningful change and inspire others to follow suit.
In the next section, we will explore emerging trends and future possibilities in sustainable web design, paving the way for a more environmentally conscious digital landscape.
The Future of Sustainable Web Design
Emerging Trends and Innovations
The field of sustainable web design continues to evolve, with new trends and innovations reshaping the future of digital sustainability. Let’s explore some key developments that are shaping the future of web sustainability:
1. Green Hosting and Data Centers
Hosting providers and data centres increasingly prioritise renewable energy sources and implement sustainable practices. The use of solar and wind energy, efficient cooling systems, and carbon offsetting are becoming more prevalent, reducing the environmental impact of website hosting.
2. Sustainable Web Development Frameworks and Tools
Developers are creating frameworks and tools specifically designed for sustainable web development. These tools enable streamlined coding, resource optimisation, and energy-efficient rendering, making it easier for web designers to incorporate sustainability into their projects.
3. Design for Circular Economy
The circular economy, which minimises waste and maximises resource efficiency, is gaining traction in design. Designers are embracing techniques like modular design, reusability of components, and upcycling of existing energy and material resources to create sustainable websites.
4. AI-Driven Energy Optimisation
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a significant role in optimising energy efficiency in web design. AI-powered algorithms can analyse and optimise code, automate image compression, and dynamically adjust website performance to reduce energy use while maintaining optimal user experiences.
The Global Impact of Sustainable Web Design
The adoption of sustainable design practices has the potential to make a significant global impact:
1. Reducing Carbon Footprint
By implementing sustainable strategies, designers can significantly reduce the carbon footprint of websites and digital services. This collective effort can contribute to mitigating climate change and preserving natural resources.
Measuring our Impact with Online Tools
It can be challenging to gauge the success of sustainability initiatives, and it depends on what we want to assess specifically. Using tools like the Website Carbon Calculator, EcoPing, and Beacon, we can get an overall sense of how changes to our digital products might impact the environment. By comparing the quantity of CO2 emitted to everyday actions like driving, heating water, or watching a film, these tools are handy for making the impact more relatable.
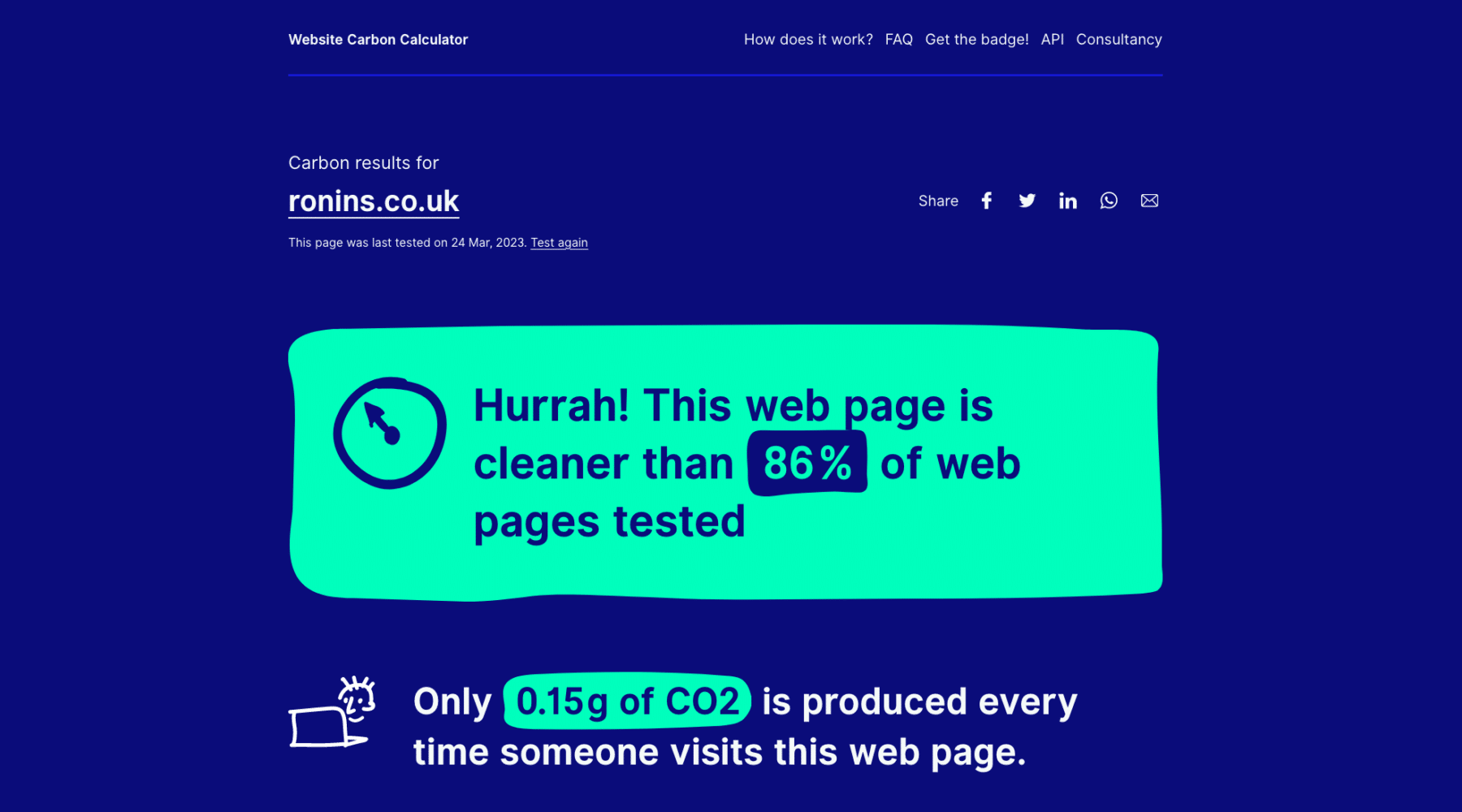
In an effort to minimise our website’s environmental impact, we’ve paid particular attention to web technology. The Website Carbon Calculator by Wholegrain Digital shows that Ronins’ homepage is cleaner than 86% of pages tested.
2. Promoting Environmental Awareness
Sustainable design provides an opportunity to raise awareness about environmental issues. Websites can educate visitors about sustainability, showcase eco-friendly practices, and inspire positive actions for a greener future.
3. Encouraging Industry-wide Adoption
As sustainable web design gains prominence, it has the potential to become an industry standard. By sharing success stories, best practices, and resources, the design community can foster a culture of sustainability and encourage widespread adoption.
4. Empowering Users for Sustainable Choices
Sustainable web design can empower users by providing them with information, tools, and resources to make more sustainable choices. Websites can promote eco-friendly products, services, and lifestyles, facilitating positive change on an individual level.
By embracing emerging trends and recognising the global impact of sustainable web design, we can collectively create a digital landscape that’s environmentally conscious, user-friendly, and socially responsible.
• • •
Taking Action for a Greener Online Future
Building a Sustainable Digital Landscape
As we conclude our exploration of sustainable web design, we must reflect on the significance of our collective actions in shaping a greener online future.
Embracing Responsibility and Impact
Sustainable web design is not merely a trend but a responsibility that designers, developers, and stakeholders must embrace. By recognising the impact of our digital footprint, we can prioritise sustainability and make a positive difference.
The Power of Collaboration
Creating a sustainable digital landscape requires collaboration among individuals, organisations, and the industry as a whole. By sharing knowledge, resources, and best practices, we can inspire one another and drive meaningful change.
• • •
Our Call to Action
The time for action is now. Let’s take the principles and strategies of sustainable web design and turn them into tangible outcomes. Here are some key steps we can take:
1. Educate and Raise Awareness
Sustainable web design is becoming more widely discussed. By spreading the knowledge of sustainable web design, we can raise awareness within the industry and beyond. Let’s educate others about the importance of minimising our environmental impact and the role of sustainable practices in web design.
2. Implement Sustainable Strategies
Put theory into practice by incorporating sustainable strategies in your web design projects. Optimise energy efficiency, minimise resource usage, prioritise user experience, and design with accessibility and inclusivity in mind.
3. Collaborate and Share Success Stories
Join forces with like-minded individuals and organisations. Collaborate, share success stories, and promote sustainable web design initiatives. Together, we can inspire others and accelerate the adoption of sustainable practices.
4. Advocate for Change
Advocate for sustainability in the web design industry. Encourage industry associations, conferences, and platforms to prioritise sustainability and promote sustainable web design as a standard practice.
Creating a Greener Online Future
Sustainability is a powerful tool to create a greener online future. By integrating eco-conscious practices, optimising energy efficiency, and prioritising user experiences, we can build digital products that positively impact the environment and society.
As designers and digital creators, we have the opportunity and responsibility to shape a more sustainable digital landscape. By embracing sustainability opportunities and working together, we can create a digital world that fosters environmental stewardship, inclusivity, and a brighter future for all.
• • •
Further reading
Feel free to explore these articles to deepen your knowledge of sustainable web design.
- Recommended articles, podcasts, communities and more regarding green UX/UI Design: https://greentheweb.com/recommended-links/
- What is Sustainable Web Design and How to Achieve It https://www.kualo.co.uk/blog/sustainable-web-design
- Green UX: Is your UI harming the environment? The article provides an overview of sustainable web design and how to make better decisions as a UX designer.
- Using Ethics In Web Design Ethical thinking was the cornerstone of the internet, yet somehow it got lost. What can you do to bring them back? What are the right questions, methods and tools?